Radiance
Table of contents
Definition
Radiance is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a surface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area. It is used as a measure of the intensity of light travelling in a particular direction.
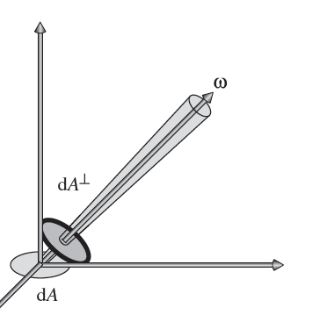
The image below shows a direction \(\omega\) and a surface element \(dA^\perp\) that’s perpendicular to \(\omega\). This is the projected area.
\[L = \frac{d^2 \Phi}{dA^\perp d\omega} = \frac{d^2 \Phi}{dA \cos \theta d\omega}\]It is measured in \(\text{Watt}/ m^2 sr\).
Usefull Properties for Ray Tracing
- Radiance is constant along rays that travel trough empty space and is also the same in both directions. (It is only when we use color filtering that the radiance changes along the rays.)
- As it can be defined at any point in space, not just on surfaces, it can be defined at the eye point of a pinhole camera, or a point on a pixel.
- If the point is on a surface, the radiance doesn’t depend on whether the flux is arriving at or leaving the surface.