BRDFs
Table of contents
Definition
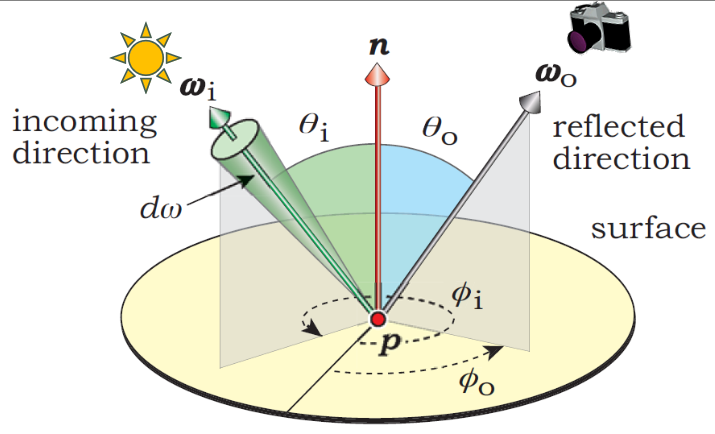
We need a way to precisely describe how light is reflected at surfaces. The bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) is a function that describes how light is reflected at a surface. It is a function that takes two directions and a point as input and returns a value that ranges from 0 to infinity. An example of a BRDF that is infinite is a mirror.
\[f_r(p, \omega_i, \omega_o) = \frac{dL_o(p, \omega_o)}{L_i(p, \omega_i) \cos \theta_i d\omega_i}\]where
- \(f_r\) is the BRDF which has the units \(\frac{1}{sr}\) (inverse steradian)
- \(\omega_i\) is the incident direction
- \(\omega_o\) is the outgoing direction
- \(p\) is the point on the surface
- \(L_i\) is the incoming radiance
- \(L_o\) is the outgoing radiance
Properties
- Reciprocity: \(f_r(p, \omega_i, \omega_o) = f_r(p, \omega_o, \omega_i)\)
- Energy conservation: \(\int_{\Omega} f_r(p, \omega_i, \omega_o) \cos \theta_i d\omega_i \leq 1\) (all outgoing energy is less than the incomping energy, since some energy is absorbed e.g. as heat))
- Linearity: Materials often need multiple BRDFs to model their reflective properties. In this case, the total BRDF is the sum of the individual BRDFs.